For years, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have been celebrated for their transparency. Every on-chain transaction, every governance vote, and every treasury movement is visible to anyone with a blockchain explorer. While this openness builds trust, it also creates massive risks. DAOs often manage treasuries worth millions, making them prime targets for attackers and front-runners. The push for confidential DAO treasury management is more than just a trend – it’s becoming a necessity.
Why Confidentiality Matters in DAO Treasuries
The classic DAO treasury model relies on public smart contracts to hold and distribute funds. Anyone can verify balances or track payments in real time. But as the ecosystem matures, this radical transparency has downsides:
- Security threats: Publicly visible treasuries attract hackers and scammers.
- Competitive disadvantage: Strategic moves (like investments or partnerships) can be front-run by competitors.
- User privacy: Members may not want their voting choices or payment addresses exposed to the world.
If DAOs want to operate at scale while protecting users and strategies, they need privacy solutions that don’t sacrifice verifiability or trust.

The Role of Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) in Private DAO Governance
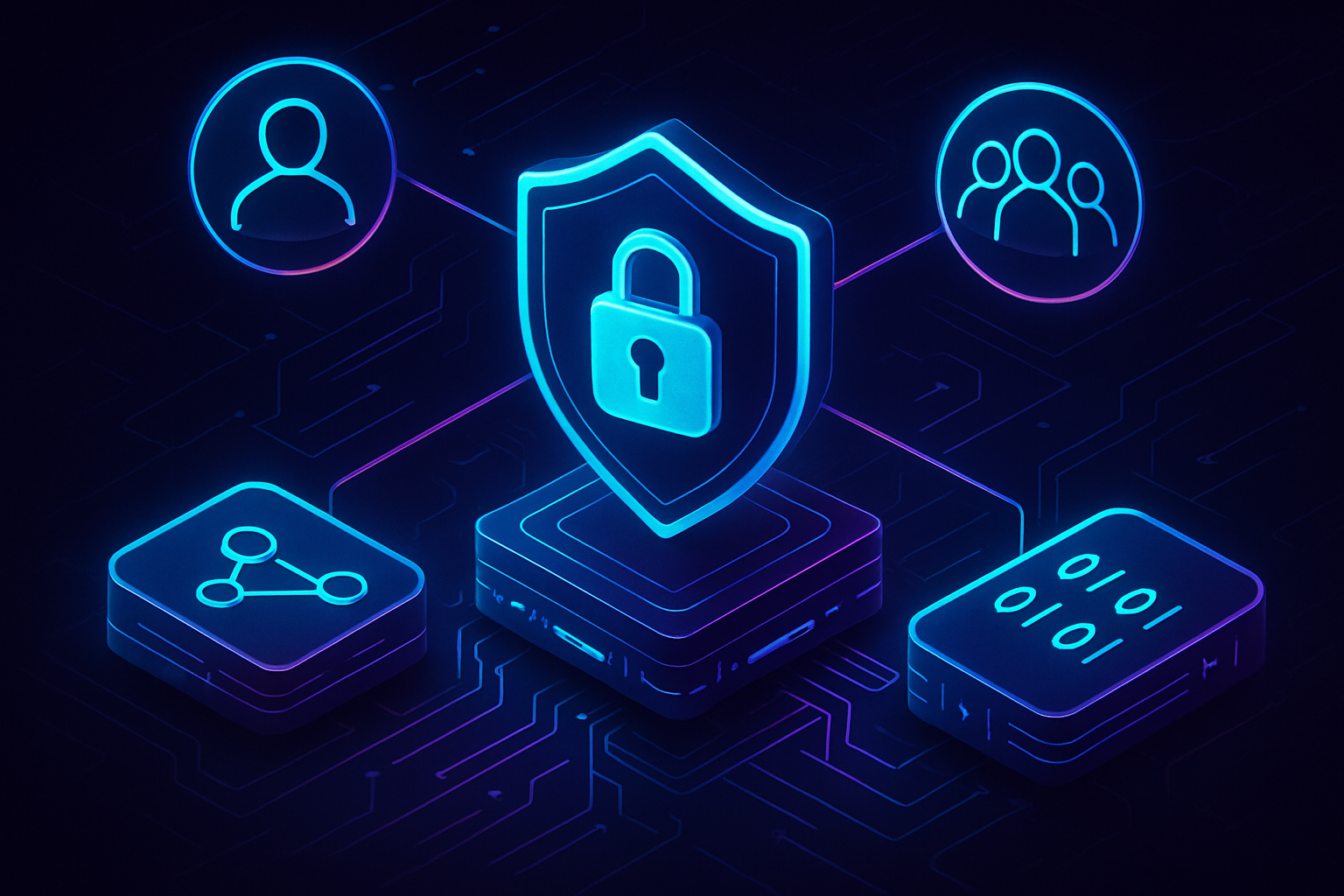
This is where Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) enters the scene. FHE allows computations to be performed directly on encrypted data – meaning smart contracts can process votes, transactions, or proposals without ever decrypting sensitive information. The data remains private, but the results are still publicly verifiable.
Zama’s fhEVM is pioneering this technology for Ethereum-compatible chains (source). In an FHE-powered confidential DAO treasury:
- Treasury transactions are encrypted end-to-end. Only authorized parties see details like amounts and recipients.
- Governance votes are cast privately; no one knows how you voted except you.
- Treasury operations, like funding new projects or rebalancing assets, remain auditable via cryptographic proofs without exposing sensitive data.
How Confidential Treasury Management Actually Works
The mechanics behind a confidential DAO treasury are both elegant and powerful:
Key Steps in a Confidential DAO Treasury Workflow
-

1. Encrypt Treasury Data Using FHEAll treasury balances, transaction details, and voting inputs are encrypted with Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) before being stored or processed on-chain. This ensures sensitive information remains private, even as computations occur.
-

2. Propose Treasury Actions PrivatelyMembers submit proposals for spending, investment, or fund allocation. Proposal details (amounts, recipients) are encrypted, allowing only authorized participants to view sensitive information while maintaining transparency of the proposal process.
-

3. Conduct Confidential VotingDAO members cast their votes on treasury proposals through encrypted ballots, leveraging FHE-based voting platforms such as Zama’s fhEVM. This ensures individual choices remain private, while the aggregate result is verifiable.
-

4. Execute Encrypted TransactionsUpon approval, treasury transactions (transfers, swaps, investments) are executed directly on encrypted data. The amounts and recipient addresses stay confidential, but the correctness of operations can be verified by all members.
-
5. Publicly Verify Outcomes Without Revealing DataMembers and auditors can verify that treasury actions and voting were performed correctly using verifiable computation proofs generated by FHE. This maintains trust and transparency without exposing underlying sensitive information.
Let’s break down what happens under the hood:
- User submits an encrypted proposal or transaction request. This could be a funding allocation, payment approval, or governance vote – all encoded with FHE so no raw data is leaked on-chain.
- The smart contract processes these encrypted inputs. Instead of decrypting them (which would expose sensitive info), it computes directly on ciphertexts using FHE-enabled logic provided by platforms like Zama’s fhEVM.
- The output – such as vote tally results or transaction approvals – is published with cryptographic proofs. Anyone can verify these proofs match the encrypted inputs without learning any private details about who voted what or which address received funds.
This approach unlocks a new level of privacy-preserving governance where trust doesn’t require full transparency of every detail – only verifiable outcomes based on sound math.
The Balance: Privacy Without Sacrificing Trust
You might wonder: if everything is hidden, how do we know there’s no foul play? That’s where the magic of verifiable computation comes in. With FHE-based systems, DAOs can publish zero-knowledge proofs alongside every action. These cryptographic attestations allow anyone to check that rules were followed – even if they never see individual votes or transaction amounts themselves.
For members, this means you can participate in governance or propose treasury actions with confidence that your privacy is protected, yet the process remains accountable and tamper-resistant. The result: a treasury that’s both shielded from prying eyes and immune to backroom manipulation. It’s a powerful shift in the DAO trust model, moving from “trust us because it’s public” to “trust the math, not the messenger. ”
Emerging Use Cases and Real-World Examples
Confidential treasury management isn’t just theoretical. DAOs are already experimenting with FHE-powered workflows for everything from grant disbursements to confidential voting on high-stakes proposals. For example, Zama’s fhEVM is enabling Ethereum-compatible DAOs to run private, auditable ballots and handle encrypted payments, all without exposing sensitive operational details (source).
Meanwhile, projects like FHE State OS are pushing further, building decentralized identity systems that keep personal data encrypted on-chain while still allowing verifiable access control. This opens the door for DAOs to manage not just funds, but also membership and credentialing, in a privacy-preserving way.
Challenges on the Road to Adoption
Despite the promise, deploying FHE for DAOs comes with technical and cultural hurdles. FHE computations are still more resource-intensive than traditional on-chain logic, which can slow transaction times and increase costs. Integration with legacy DAO tooling isn’t always seamless, and user education is needed to help members understand the new privacy guarantees, and their limits.
Yet, the cryptography community is moving fast. Protocols are being optimized, and hybrid approaches (combining FHE with other privacy tech like zero-knowledge proofs) are making confidential treasury management more practical by the month. As these tools mature, expect more DAOs to adopt confidential workflows, not just for treasury management, but for all forms of sensitive governance.
DAO Treasury Confidentiality: Pitfalls & Best Practices
-

Underestimating FHE’s Computational Overhead: Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) is powerful but resource-intensive. Many DAOs overlook the performance impact and increased costs associated with FHE-based treasury operations. Best Practice: Use solutions like Zama’s fhEVM that are optimized for blockchain environments and regularly benchmark performance before scaling.
-

Neglecting User Experience in Confidential Voting: Complex cryptographic processes can confuse DAO members and reduce participation. Best Practice: Integrate user-friendly interfaces, such as those offered by Snapshot (with FHE add-ons), to ensure seamless and private voting.
-
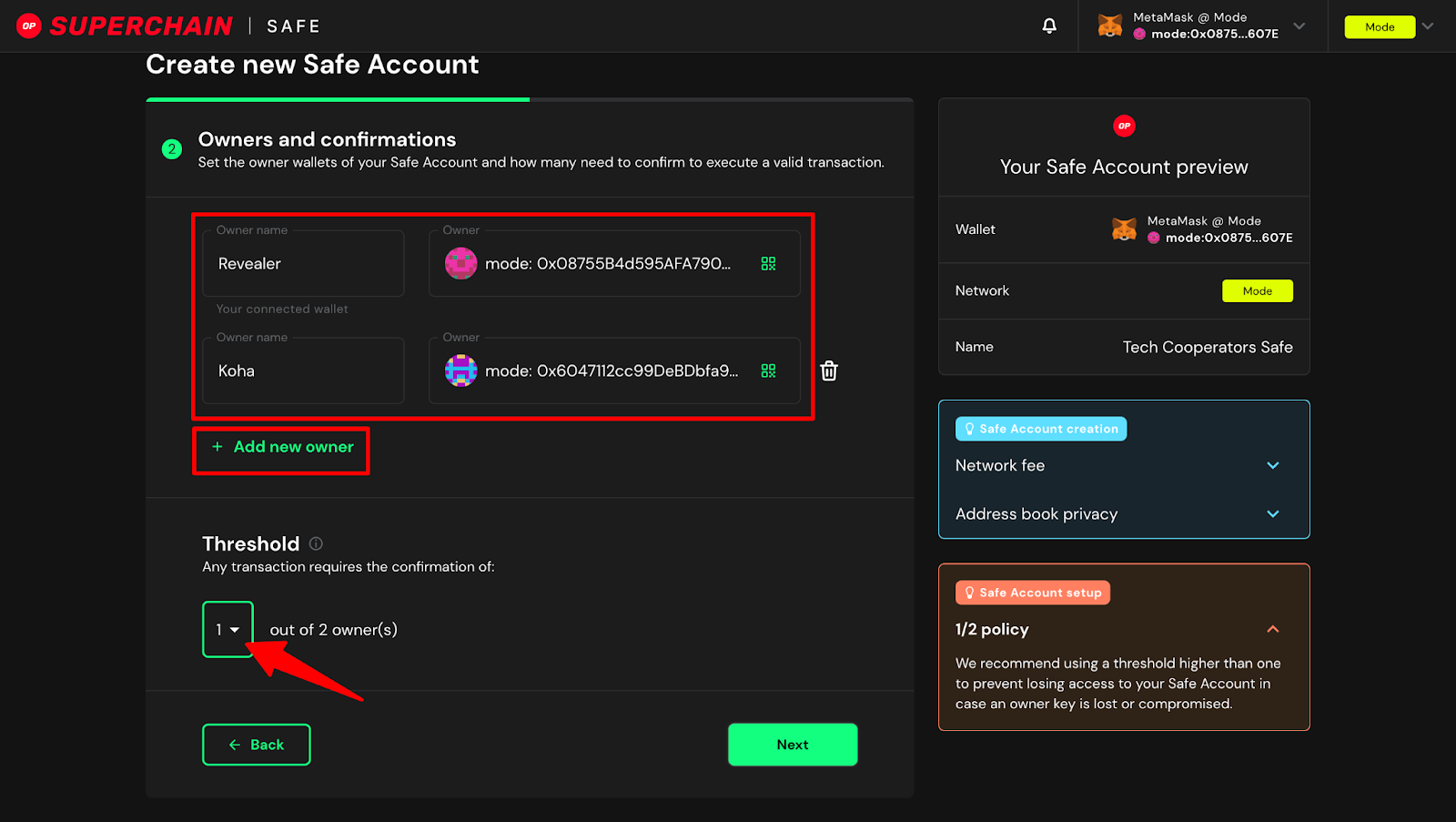
Inadequate Key Management: Poor handling of encryption keys can compromise both confidentiality and access to treasury funds. Best Practice: Implement multi-signature wallets (e.g., Gnosis Safe) and decentralized key management protocols to securely distribute control.
-

Failing to Balance Transparency and Privacy: Overly opaque operations can erode trust, while too much transparency exposes sensitive data. Best Practice: Use FHE to keep transaction details private but publish verifiable proofs (e.g., zero-knowledge proofs) for all treasury actions.
-

Lack of Regular Security Audits: New cryptographic implementations can introduce vulnerabilities. Best Practice: Partner with reputable security firms like Trail of Bits or ConsenSys Diligence to audit smart contracts and encryption logic regularly.
-

Ignoring Regulatory Compliance: Confidential treasuries must still adhere to local and international regulations. Best Practice: Consult with legal experts and use compliance-focused platforms such as Chainalysis for transaction monitoring and reporting.
The Future of Confidential DAO Treasuries
Looking ahead, the trend is clear: as DAOs scale, privacy will be as fundamental as transparency. Confidential treasury management isn’t about hiding wrongdoing, it’s about protecting legitimate strategies, member privacy, and organizational resilience in an increasingly adversarial environment.
Imagine a world where DAOs can:
- Allocate grants or invest in new projects without tipping off competitors
- Let members vote on sensitive issues without fear of retaliation or doxxing
- Prove compliance and fairness with cryptographic evidence, not just open ledgers
That’s the promise of FHE for DAOs: private DAO governance that’s still open to audit and scrutiny, just on cryptographic terms, not at the expense of member safety or treasury security.
For founders, treasury managers, and DAO contributors, now is the time to learn how these tools work and what they mean for your organization’s future. The next generation of DAOs won’t just be transparent, they’ll be confidential, resilient, and ready for anything.






