Privacy is rapidly becoming the cornerstone of next-generation decentralized governance. As DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) mature, their need for confidential operations grows – especially in voting, proposal creation, and treasury management. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are emerging as the gold standard for enabling private DAO governance, offering a path to secure participation without compromising transparency or trust.
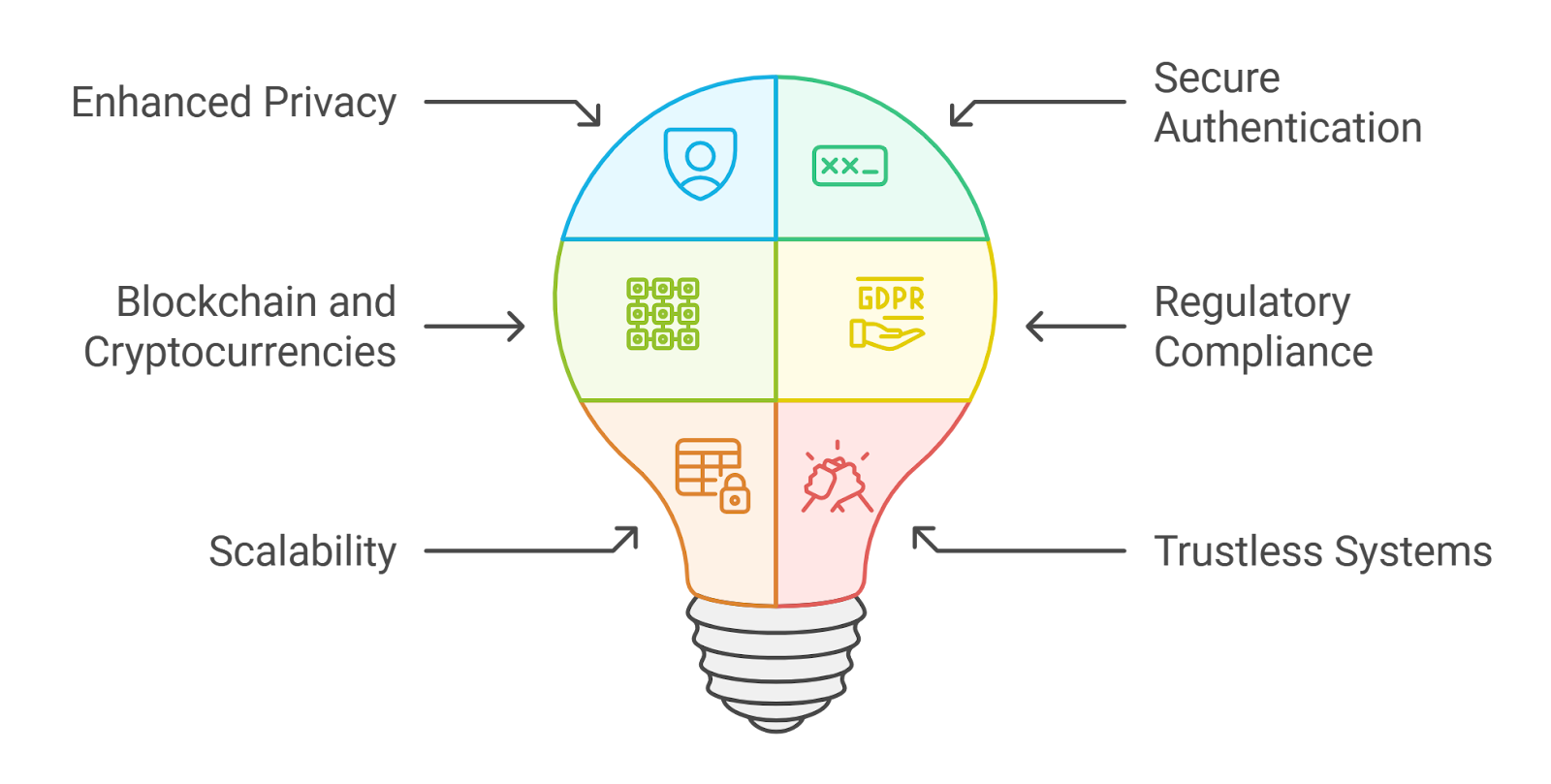
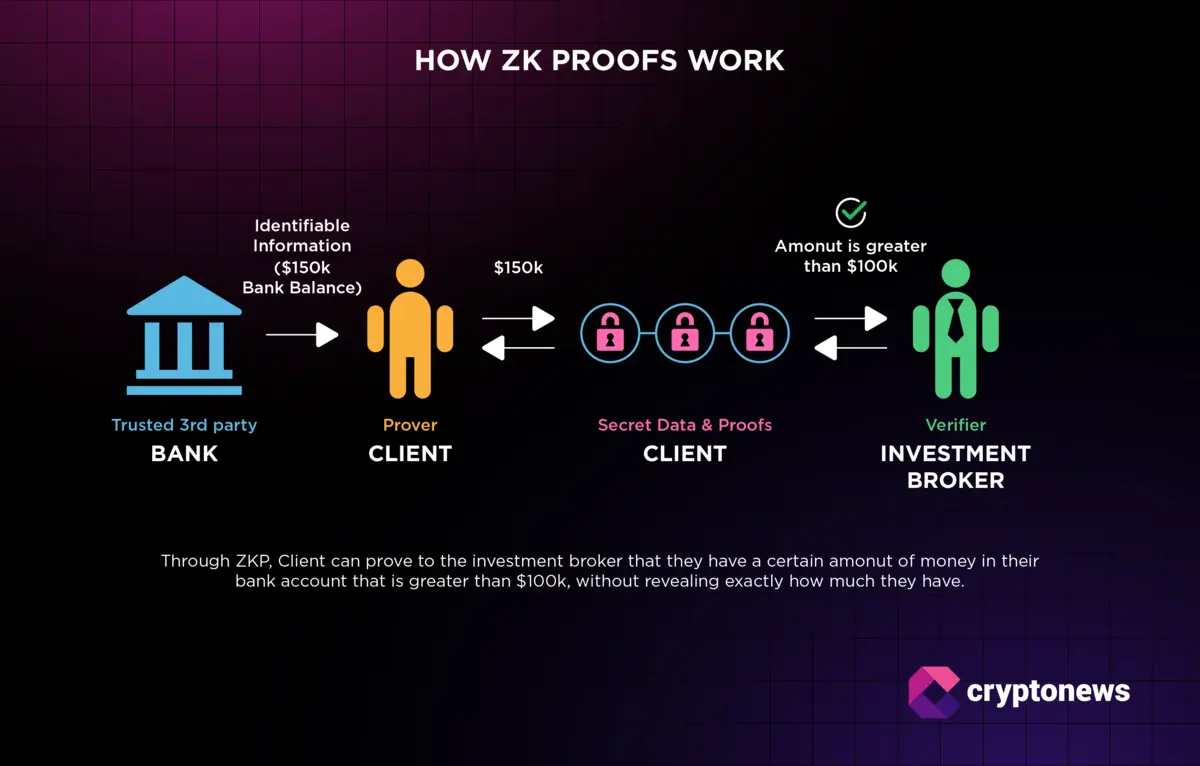
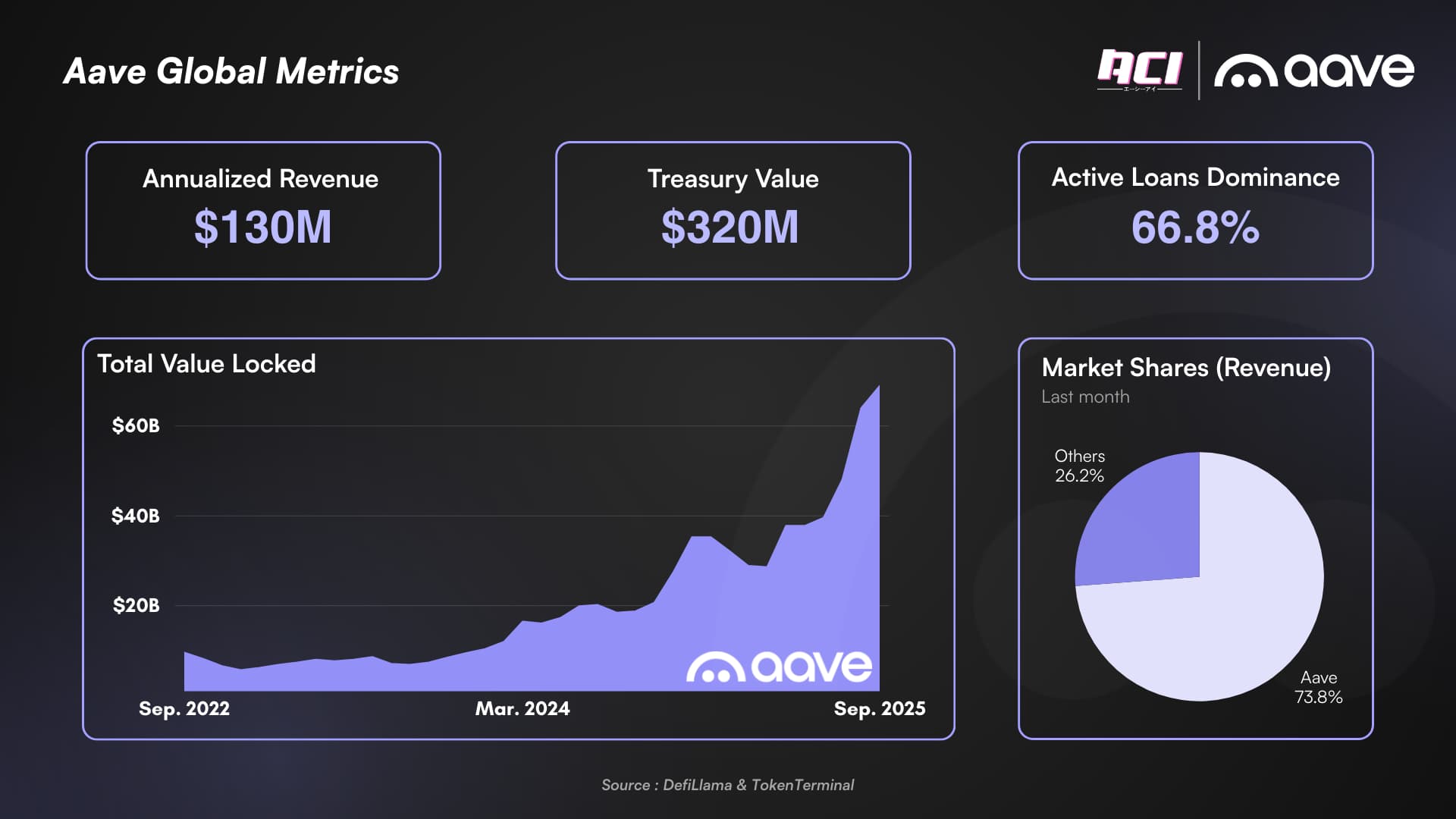
At its core, a zero-knowledge proof allows someone to prove they know a fact or meet a condition without revealing any underlying information. This cryptographic technique is already transforming how DAOs manage sensitive processes on-chain. With Ethereum trading at $3,996.57, and DAO treasuries holding billions in digital assets, the stakes for robust privacy solutions have never been higher.
Why Privacy Matters in DAO Governance
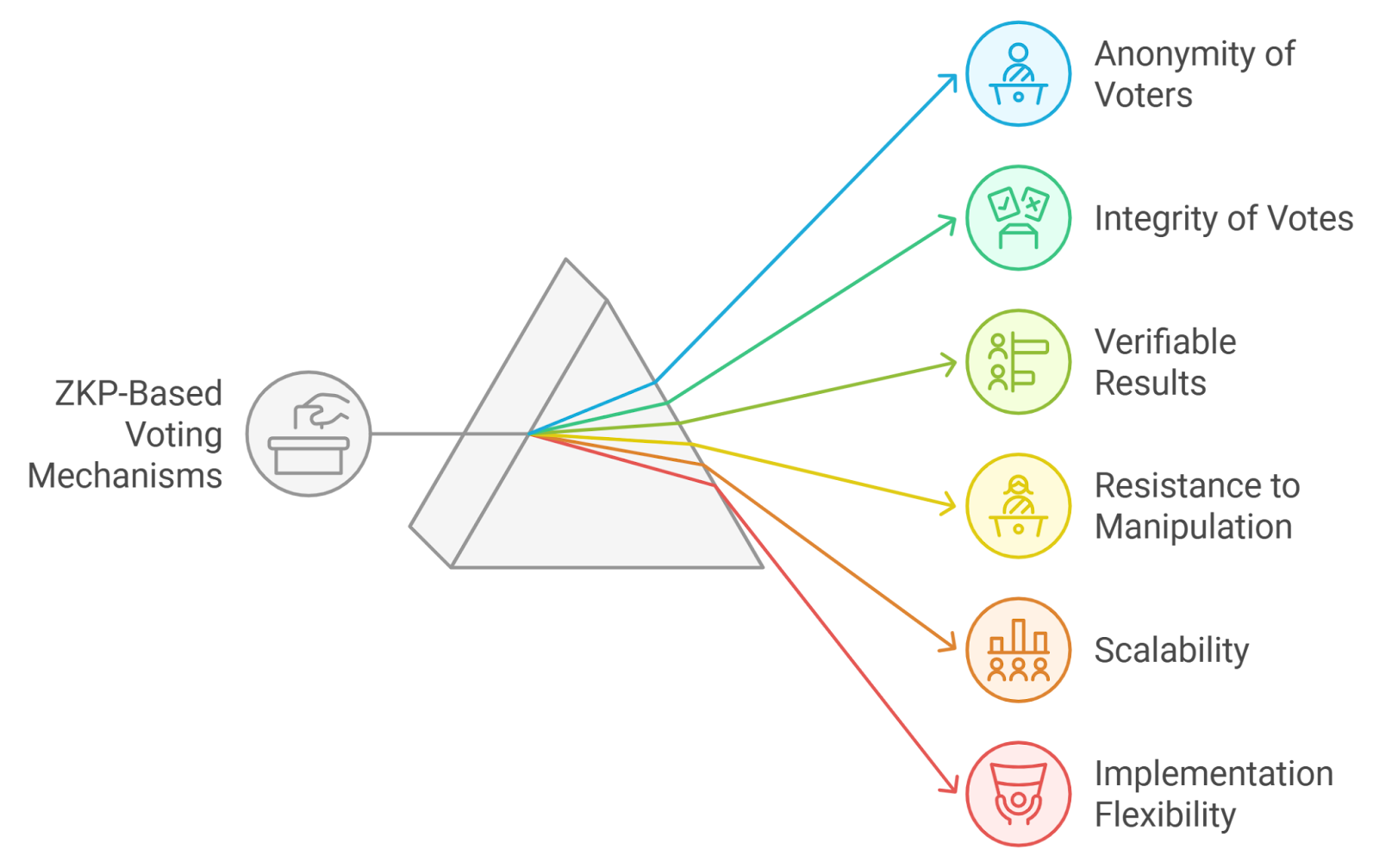
Open blockchains are powerful but unforgivingly transparent. Every transaction and vote is visible to all – which can expose members to coercion, retaliation, or manipulation. The result? Participation drops and governance becomes vulnerable to bad actors. Zero-knowledge proofs solve this by letting participants prove eligibility or cast votes without exposing their identity or preferences.
For example, projects like CIL Private DAO have adopted ZKPs to ensure fully anonymous voting. Members can participate freely, knowing that neither their vote nor their identity will be revealed until consensus is reached – if at all.
The Building Blocks: How ZKPs Work in Practice
There are several flavors of zero-knowledge proofs used in blockchain today:
ZK-SNARKs vs. ZK-STARKs for Private DAO Governance
-
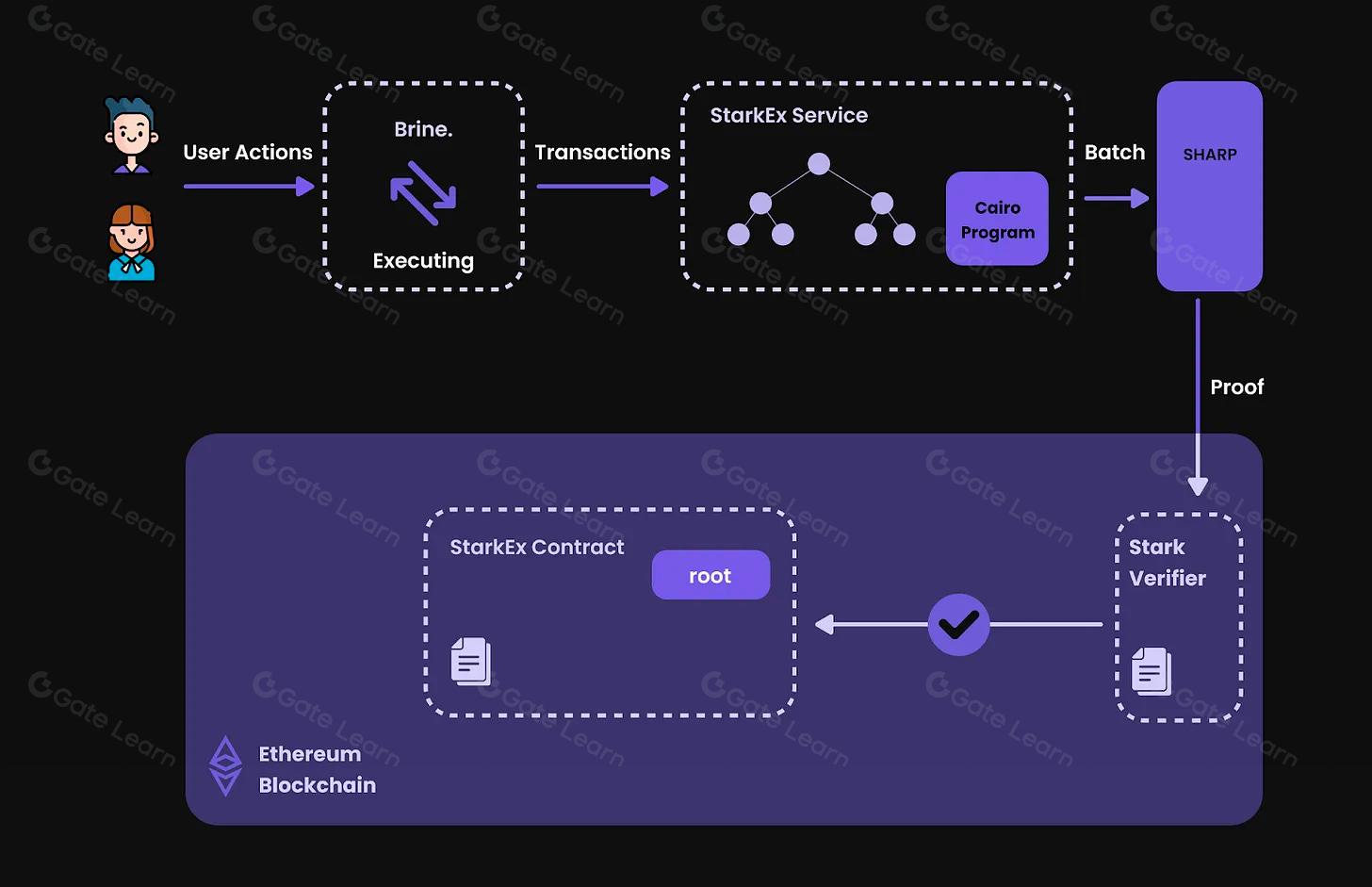
ZK-SNARKs: Small Proof Size & Fast VerificationZK-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) generate compact proofs that are quick to verify, making them suitable for blockchain environments like Ethereum. However, they require a trusted setup, which introduces a one-time security risk if not handled properly. ZK-SNARKs are widely used in privacy-focused projects such as Zcash and Aztec, and are being integrated into DAO voting platforms to enable confidential voting and proposal creation.
-
ZK-STARKs: Transparent Setup & Quantum ResistanceZK-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge) offer a transparent setup that eliminates the need for trusted parties, enhancing trust and auditability. They are also resistant to quantum attacks, providing future-proof security. The trade-off is larger proof sizes and higher computational requirements, which can impact scalability for DAOs. ZK-STARKs are being adopted by platforms like StarkWare and Immutable X for privacy-preserving applications, including DAO governance.
-

Trusted Setup vs. Transparency: Security ImplicationsZK-SNARKs require a trusted setup ceremony to generate cryptographic parameters, which, if compromised, could undermine the system’s integrity. In contrast, ZK-STARKs use transparent setup processes, reducing the risk of hidden vulnerabilities and increasing trust among DAO members.
-
Performance & Scalability: Proof Size and ComputationZK-SNARKs are favored for their small proof sizes and low verification costs, making them efficient for on-chain DAO operations. ZK-STARKs, while more scalable in theory, produce larger proofs and require more computation, which can increase gas costs and slow down DAO voting or proposal execution.
-
Adoption in DAO Governance: Real-World IntegrationsProjects like CIL Private DAO and Private Voting DAO on Aleo are leveraging ZK-SNARKs for private voting and proposal creation. Meanwhile, StarkWare’s technology, based on ZK-STARKs, is being explored for scalable, privacy-preserving DAO frameworks. The choice between these technologies depends on a DAO’s specific needs for privacy, scalability, and trust.
ZK-SNARKs require a trusted setup but produce small proof sizes and fast verification times – making them popular for Ethereum-based confidential voting systems. ZK-STARKs, on the other hand, offer transparency with no trusted setup but generate larger proofs. The choice depends on your DAO’s priorities: efficiency versus setup complexity.
Integration with smart contracts is another technical hurdle. Tools like Circom and SnarkJS help developers embed these cryptographic proofs into DAO voting logic on Ethereum or other EVM chains (source). But it’s not just about code – it’s about creating seamless user experiences so that every member can participate securely without deep technical knowledge.
Key Applications of Zero-Knowledge Proofs in DAOs
- Anonymous Voting: Members cast votes privately, protecting against vote buying and intimidation.
- Private Delegation: Protocols like Kite let users delegate power without revealing relationships (arXiv.org).
- Confidential Proposal Creation: Anyone can propose initiatives without fear of bias or retaliation.
- Treasury Privacy: Sensitive financial actions remain hidden from public view while staying auditable by authorized parties.
This multi-layered approach enables DAOs to strike a balance between transparency for accountability and privacy for protection – crucial as more institutional capital flows into the ecosystem at current ETH price levels ($3,996.57) and beyond.
Yet, implementing zero-knowledge proofs in DAO governance is not without its challenges. The computational demands of generating and verifying ZKPs can introduce latency and increase on-chain costs, particularly as the scale of participation grows. For DAOs with thousands of members and complex voting schemes, optimizing these cryptographic operations is essential to maintain both privacy and usability.
Another crucial factor is the user experience. While ZKPs are mathematically elegant, their technical complexity can be daunting for non-developers. If we expect widespread adoption of confidential DAO voting, interfaces must abstract away the cryptography, offering intuitive workflows that empower users to participate securely with minimal friction. Projects like MACI (Minimal Anti-Collusion Infrastructure) are already making strides by encrypting votes and using zero-knowledge proofs to verify results without exposing sensitive data.
Best Practices for Private DAO Governance
Best Practices for Implementing ZK Proofs in DAOs
-

Prioritize Anonymous Voting Mechanisms: Adopt established solutions like CIL Private DAO to enable members to cast votes confidentially, reducing risks of vote buying and intimidation while maintaining trustless verification.
-
Enable Private Delegation Protocols: Integrate privacy-preserving delegation systems such as Kite, allowing members to delegate, revoke, or re-delegate voting power without exposing delegate relationships.
-

Utilize ZKPs for Secure Proposal Creation: Leverage open-source tools like Private Voting DAO (Aleo) to let members submit proposals anonymously, fostering unbiased and open participation.
-

Protect Treasury Actions with Confidential ZKPs: Implement zero-knowledge proofs in treasury management to execute sensitive financial actions privately, as demonstrated by Private Voting DAO (Aleo).
-

Choose the Appropriate ZKP Technology: Evaluate ZK-SNARKs (smaller proofs, trusted setup) versus ZK-STARKs (transparent setup, larger proofs) based on your DAO’s privacy, scalability, and trust requirements.
-
Integrate ZKPs with Smart Contracts Using Proven Tools: Employ frameworks like Circom and SnarkJS to design, generate, and verify zero-knowledge proofs within Ethereum-based smart contracts.
-
Optimize for User Experience: Develop intuitive interfaces that abstract ZKP complexities, ensuring members can participate in governance without technical barriers.
-
Monitor Computational Overhead and Costs: Regularly assess the resource demands of ZKP operations to maintain efficient, cost-effective DAO governance, especially as Ethereum (ETH) price is currently $3,996.57 with recent fluctuations.
For founders and contributors seeking to build robust privacy into their organizations, consider these strategic recommendations:
- Assess Your Threat Model: Identify where privacy risks are highest, voting, proposals, or treasury, and prioritize accordingly.
- Select the Right ZKP Technology: Balance trusted setup requirements against proof size and verification speed. ZK-SNARKs may suit smaller DAOs; ZK-STARKs offer greater transparency for larger or more public communities.
- Invest in UX: Ensure your front-end experience shields users from cryptographic complexity while maintaining security guarantees.
- Audit and Monitor: Regularly review smart contracts, cryptographic circuits, and off-chain infrastructure for vulnerabilities.
- Stay Informed: The field evolves rapidly, follow leading projects and research to keep your governance stack resilient.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Secure Decentralized Governance
The momentum behind zero-knowledge proofs in DAOs signals a new era where privacy is integral, not optional, to decentralized coordination. As Ethereum remains strong at $3,996.57, DAOs are poised to attract more mainstream users who demand both empowerment and protection. Expect further breakthroughs as open-source tools mature, hardware acceleration reduces costs, and standards emerge around confidential governance protocols.
The next generation of private DAOs will likely blend ZKP-powered voting with advanced identity systems, enabling anonymous participation without sacrificing sybil resistance or regulatory compliance. Confidential treasury management will unlock new use cases for institutional investors wary of public financial exposure but eager to participate in decentralized ventures.
If you’re building or joining a DAO today, prioritize privacy from day one. It’s not just about hiding information, it’s about fostering trust, encouraging candid participation, and future-proofing your community against evolving threats.
Diversify your privacy tools. Protect member autonomy. Prosper through secure governance.






