In the rapidly evolving landscape of decentralized governance, privacy is no longer a luxury – it is a necessity. Traditional on-chain voting systems in DAOs have exposed members to manipulation, coercion, and even bribery, fundamentally undermining the democratic ideals these organizations aspire to. The emergence of private voting protocols is now transforming confidential DAO governance, offering innovative cryptographic guarantees that protect both voter intent and organizational integrity.

The Case for Privacy in DAO Voting
Open ballots may seem transparent, but in practice they create vulnerabilities. Public vote disclosures allow powerful actors (“whales”) to exert undue influence, while peer pressure and strategic voting can distort outcomes. As highlighted by research from pse. dev and DL News, most DAOs today lack robust privacy mechanisms – making them susceptible to both subtle manipulation and overt corruption.
Private voting DAOs address these risks by ensuring that votes remain confidential throughout the decision-making process. This not only prevents voter intimidation but also encourages honest participation, unlocking the full potential of decentralized governance. By shielding individual choices from public scrutiny until results are finalized, private voting protocols foster a more equitable environment where every member’s voice is protected.
Key Technologies Powering Confidential Governance
The transition toward confidential governance blockchain solutions has been catalyzed by several cutting-edge technologies:
Key Cryptographic Tools Powering Private DAO Voting
-
Shielded Voting (Shutter Network): Encrypts votes during active proposals, revealing results only after voting concludes to prevent manipulation and ensure voter privacy.
-
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (Kite Protocol): Enables private delegation and voting, allowing participants to prove eligibility and participation without disclosing choices or identities.
-
Homomorphic Encryption (Zama, Shutter Network): Allows encrypted votes to be tallied without decryption, maintaining confidentiality while ensuring verifiable results.
-

Trusted Execution Environments (Oasis Network): Processes votes within secure hardware enclaves, safeguarding data integrity and privacy throughout the voting lifecycle.
-
Self-Tallying Protocols (BVOT): Utilizes multiparty threshold homomorphic encryption for decentralized, private vote tallying, ensuring ballot secrecy and fairness.
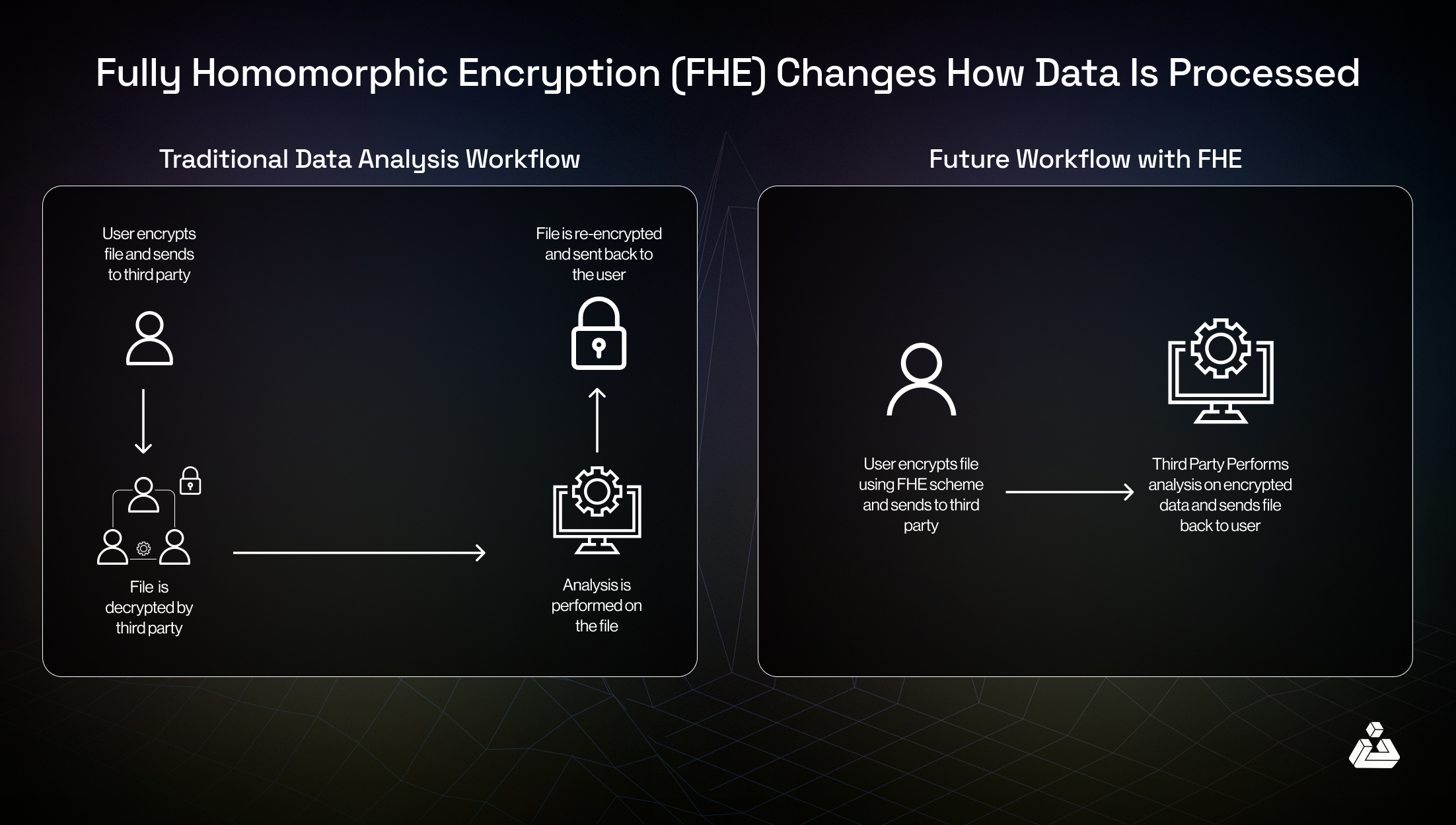
- Homomorphic Encryption (FHE): Protocols like those pioneered by Zama and Fairblock allow computations on encrypted data. Votes are cast and tallied without ever being decrypted individually, preserving both privacy and verifiability.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Platforms such as Kite enable members to delegate or revoke voting power privately. ZKPs ensure that even delegates cannot trace who voted for whom or how much power was delegated.
- Shielded Voting: Shutter Network’s approach encrypts all votes during the polling period. Only after the poll concludes are results decrypted and revealed – mitigating pre-result manipulation.
- Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): Oasis Network leverages TEEs for confidential processing of votes within secure hardware enclaves, ensuring data remains tamper-proof throughout the lifecycle.
- Self-Tallying Protocols: Innovations like BVOT combine multiparty threshold encryption with ballot secrecy – allowing results to be computed without exposing individual choices.
The Fairblock Voting Protocol: Raising the Bar for Secure DAO Governance
The Fairblock voting protocol exemplifies this new wave of secure DAO governance tools. By making encrypted voting either mandatory or optional for proposals, Fairblock empowers organizations to tailor confidentiality levels according to their unique needs. Votes remain sealed until finalization – protecting members from retaliation or collusion during the process.
This approach not only shields voter identities but also ensures that proposal outcomes reflect genuine preferences rather than external pressures. As described in recent overviews by Reflexivity Research and G11dentak, Fairblock’s integration of FHE and public-key encryption allows even high-value transactions or sensitive decisions to be conducted with uncompromising privacy guarantees.
By leveraging FHE DAO voting and advanced cryptographic primitives, Fairblock and similar protocols are redefining what is possible for on-chain private voting. This shift is not only technical but cultural: members can now participate in governance with the assurance that their votes are truly confidential, free from fear of reprisal or undue influence. Ultimately, this cultivates a more diverse and active membership base, which is essential for the long-term health of any DAO.
Unlocking New Applications for Confidential Governance
The impact of confidential voting extends well beyond basic proposal decisions. DAOs can now conduct sealed-bid auctions, manage private funding rounds, or coordinate sensitive operational changes without exposing strategic information to adversaries or competitors. For example, Oasis Network’s privacy-enabled smart contracts allow organizations to shield proposal details and selectively reveal results only to authorized parties. This granular control over information flow creates new opportunities for innovation in decentralized governance models.
Moreover, the integration of multiparty threshold cryptography and self-tallying systems means that even as DAOs scale to thousands of members, privacy and fairness remain uncompromised. These advances also address concerns raised by researchers at MIT CSAIL and Cornell about whale dominance and vote buying in public systems. By hiding individual choices and introducing cryptographic noise into final tallies, these protocols make it significantly harder for malicious actors to reverse-engineer or coerce outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite rapid progress, several challenges remain for widespread adoption of confidential governance blockchain solutions. Scalability is a core concern: homomorphic encryption and ZKPs can be computationally intensive, potentially increasing costs or slowing down real-time decision-making. However, recent optimizations in FHE libraries and hardware acceleration (such as TEEs) are closing this gap quickly.
Another challenge is usability. Voters must trust that their ballots are both private and counted correctly, a delicate balance between transparency and confidentiality. Open-source audits, verifiable cryptographic proofs, and transparent protocol design will be crucial for building trust within DAO communities.
“Private voting prevents corruption, enables more honest participation, and unlocks the full potential of decentralized governance. “
Looking ahead to 2026 and beyond, expect further convergence between privacy-preserving computation (FHE/ZK), cross-chain interoperability, and modular DAO frameworks. As these technologies mature, confidential DAOs will be able to offer not just secure voting but also encrypted treasury management, private member onboarding processes, and confidential dispute resolution mechanisms, all while remaining fully decentralized.
Top Benefits of On-Chain Private Voting for DAOs
-

Prevents Voter Coercion and Bribery: By encrypting votes, protocols like Shutter Network’s Shielded Voting ensure that individual choices remain confidential until polls conclude, protecting members from external pressure and manipulation.
-

Enables Honest Participation: Private voting protocols such as Kite and zero-knowledge proof solutions allow members to vote or delegate power without revealing their preferences, fostering more genuine and uninfluenced decision-making.
-

Protects Voter Identity and Privacy: Solutions like Oasis Network’s confidential voting use Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) to shield voter identities and choices, reducing risks of retaliation and preserving anonymity.
-
Ensures Fair and Tamper-Proof Results: Homomorphic encryption, as implemented in Shutter Network and BVOT, allows for accurate vote tallying without exposing individual ballots, enhancing integrity and transparency of DAO governance.
-
Encourages Broader Participation: By mitigating risks of peer pressure and public scrutiny, private voting protocols lower barriers for members to engage in governance, leading to more inclusive and representative outcomes for DAOs.
Why Confidential Voting Matters Now
The absence of robust on-chain confidentiality has historically stifled the growth of essential applications within Web3, ranging from secure financial services to protected trading environments (see more here). The latest generation of protocols like Fairblock are not just theoretical, they are live in production settings today with real-world impact across DeFi treasuries, NFT collectives, grant programs, and more.
If you’re building or participating in a DAO today, integrating secure DAO governance with advanced privacy features isn’t just a technical upgrade, it’s a foundational shift toward more resilient communities where every member’s voice counts equally.






