Confidential governance models are rapidly becoming the backbone of secure and effective decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). As DAOs mature and their treasuries swell, the risks of voter manipulation, coercion, and governance attacks have never been clearer. Recent research underscores a harsh reality: non-algorithmic, off-chain voting governance can lead to significant value discounts for DAOs, while centralized or transparent voting systems invite both internal and external manipulation. In response, DAOs are deploying advanced cryptographic tools to ensure that decision-making reflects the true will of their communities, without exposing participants to undue influence.
Why Traditional DAO Governance Fails to Prevent Manipulation
Many early DAOs relied on transparent on-chain voting and token-weighted governance. While this approach delivered verifiability, it also made voter choices public, exposing members to social pressure, bribery, and the risk of vote buying. Attackers could accumulate tokens or coordinate Sybil attacks to swing outcomes in their favor, eroding trust and discouraging honest participation. This vulnerability has been exploited in high-profile cases, leading to controversial proposals passing against community interests.
Off-chain or non-algorithmic governance models fare no better. When votes are cast via forums or snapshot tools without robust privacy guarantees, whales can pressure smaller holders, and external actors can coerce dissenters. The result: a substantial discount in DAO value due to perceived governance risk. This landscape has driven demand for privacy-preserving DAO tools that shift the balance toward genuine community consensus.
Confidential Governance: The Cryptographic Arsenal
To counteract these threats, DAOs are integrating a suite of privacy technologies that protect voters while maintaining integrity. Here’s how confidential governance models address core vulnerabilities:
Essential Cryptographic Tools for Confidential DAO Governance
-
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): ZKPs enable voters to prove their vote’s validity without revealing its content, ensuring anonymity and integrity in DAO elections. Widely used in privacy-focused protocols, ZKPs make coercion and manipulation far more difficult.
-

Homomorphic Encryption: This cryptographic method allows votes to be tallied while encrypted, so individual choices remain confidential throughout the process. It is foundational for privacy-preserving voting systems in DAOs.
-

Private Delegation Protocols (e.g., Kite): Protocols like Kite allow voters to delegate, revoke, or re-delegate votes without revealing their preferences, even to the delegate. This maintains confidentiality and prevents undue influence.
-
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): Platforms such as Oasis use TEEs to process voting data in secure enclaves, ensuring confidentiality and integrity during execution and protecting against external manipulation.
-

Soulbound Tokens (SBTs): SBTs are non-transferable digital credentials that tie voting power to individual participation or achievement, reducing risks of vote buying and coercion in DAOs.
-

Reputation-Based Governance Models: By assigning voting power based on contributions and reputation rather than token holdings, this approach aligns decision-making with active participation and expertise, mitigating large-holder dominance.
-

Quadratic Voting: This system allocates voting power according to the square root of tokens held, making it costlier to accumulate influence and encouraging more democratic, broad-based participation.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): ZKPs allow voters to prove their eligibility and participation without revealing how they voted. This makes it impossible for adversaries to trace decisions back to individuals or coerce specific outcomes. Projects like Semaphore and zkVote exemplify this approach, delivering robust anonymity at scale.
Homomorphic Encryption: With homomorphic encryption, votes remain encrypted even as they are tallied. The result is an accurate outcome without ever exposing individual preferences, a leap forward for on-chain privacy. This method is especially relevant for DAOs handling sensitive proposals or high-stakes treasury actions.
Private Delegation Protocols: Protocols such as Kite enable voters to delegate power without revealing their intention or identity. Delegates cannot see which proposals they are empowered for until votes are cast, neutralizing the risk of targeted lobbying or retaliation. This preserves both flexibility and confidentiality in liquid democracy models.
Real-World Impact: Enhancing DAO Resilience
The adoption of confidential governance is already reshaping DAO security postures. By leveraging Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), platforms like Oasis protect voting data during processing, shielding it from both external hackers and malicious insiders. Soulbound Tokens (SBTs) and reputation-based models further shift influence away from pure token holdings toward active participation and expertise, making it far harder for attackers to buy control or manipulate outcomes through sheer financial power.
Quadratic voting adds another layer of defense by making additional votes progressively more expensive for large stakeholders. This mathematical mechanism democratizes participation and discourages whales from dominating decisions. Combined with encrypted DAO voting protocols, these innovations are restoring confidence in decentralized governance by making manipulation costly and coercion ineffective.
For organizations seeking practical guidance on implementing these tools, resources such as our breakdown on confidential voting verification offer actionable steps toward robust privacy without sacrificing accountability. The next half of this article will explore operational best practices and case studies demonstrating how confidential governance models are transforming real-world DAOs.
Operationalizing confidential governance in DAOs is not just a technical upgrade, it’s a cultural and strategic shift. Leading protocols are moving beyond pilot programs, deploying privacy-preserving tools as core infrastructure. This transition requires thoughtful integration with existing governance frameworks, clear communication to members, and ongoing audits to ensure both privacy and verifiability remain intact.
Best Practices for Deploying Privacy-Preserving DAO Tools
DAOs adopting encrypted voting and confidential delegation must address several practical challenges:
Best Practices for Encrypted DAO Voting & Confidential Governance
-

Implement Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Use ZKPs to allow members to prove their votes are valid without revealing their choices, ensuring anonymity and integrity in the voting process.
-
Adopt Homomorphic Encryption: Enable vote tallying on encrypted data so that individual choices remain confidential throughout the process, protecting voter privacy and preventing coercion.
-

Utilize Private Delegation Protocols (e.g., Kite): Allow voters to delegate and revoke voting power privately, so that even delegates do not know the original voter’s choices, reducing undue influence.
-
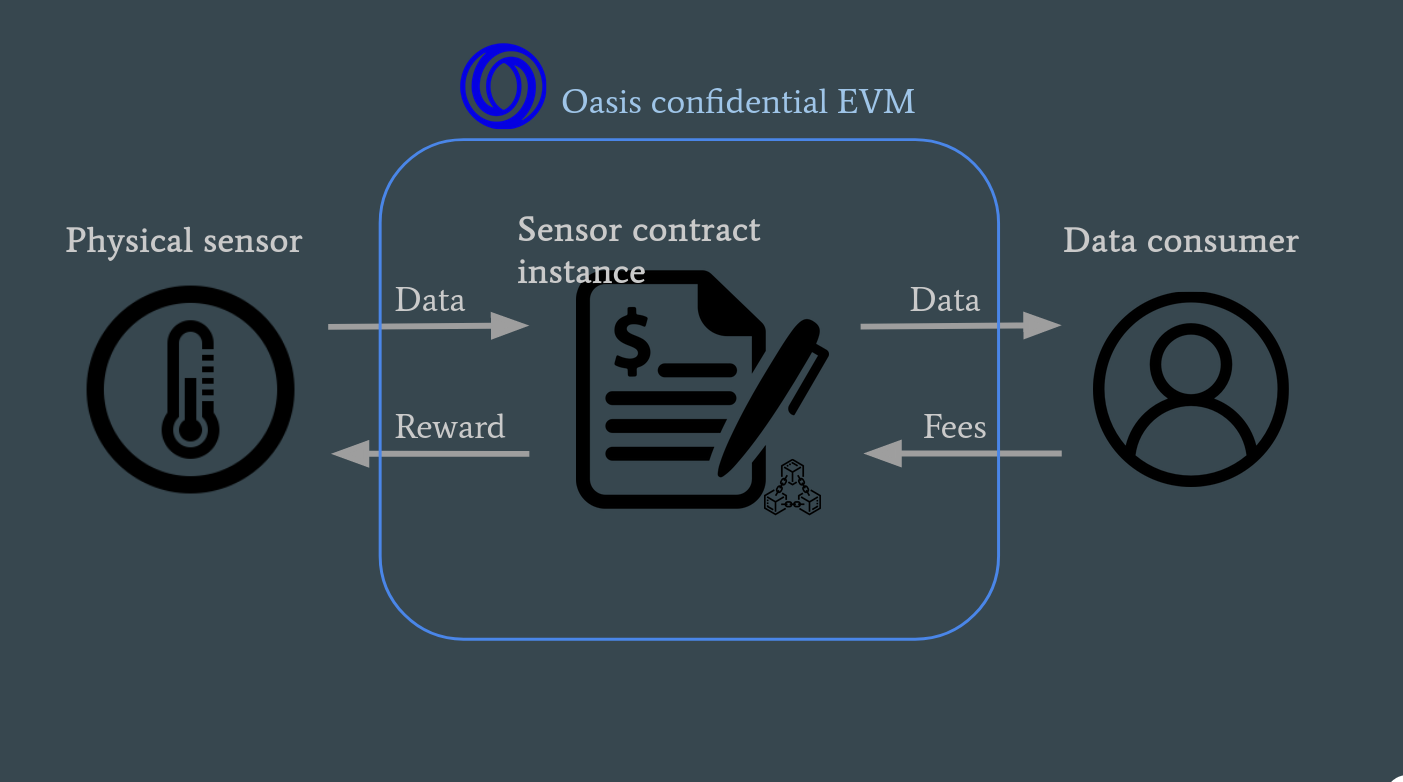
Leverage Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): Platforms like Oasis use TEEs to execute smart contracts in secure enclaves, keeping voting data confidential during processing and mitigating manipulation risks.
-

Integrate Soulbound Tokens (SBTs): Use SBTs to tie voting power to individual participation rather than token holdings, discouraging vote buying and reinforcing genuine community engagement.
-

Adopt Reputation-Based Governance Models: Assign voting power based on contributions and reputation instead of token ownership, promoting equitable and expertise-driven decision-making.
-

Implement Quadratic Voting Mechanisms: Use quadratic voting to reduce the dominance of large stakeholders and encourage broader, more democratic participation by making additional votes increasingly costly.
1. Transparent Onboarding: Educate members about how privacy tools work, why they matter, and what changes to expect in the voting process. This builds trust and reduces friction during adoption.
2. Layered Security: Combine cryptographic voting with secure proposal submission channels and regular smart contract audits. This multi-layered approach blocks both direct manipulation attempts and more subtle forms of coercion.
3. Gradual Rollouts: Pilot new confidential governance modules on non-critical votes first. Collect feedback, iterate on UX, then expand coverage to treasury decisions or sensitive proposals.
4. Community-Driven Upgrades: Allow members to propose improvements or flag vulnerabilities in privacy protocols through open forums or anonymous suggestion systems, ensuring the system evolves with emerging threats.
The Human Side: Restoring Confidence in DAO Participation
The ripple effect of confidential governance goes far beyond code. As DAOs implement privacy-preserving mechanisms, member participation rises, not just in raw numbers but in diversity of viewpoints. Anonymity emboldens minority voices who might otherwise fear retaliation or ostracism for dissenting votes. This dynamic unlocks more nuanced debates and drives smarter decision-making at scale.
Recent case studies show that DAOs using confidential voting systems report higher proposal engagement rates and fewer allegations of vote buying or collusion. In environments where financial stakes are high, such as DeFi treasuries or NFT collectives, these models are rapidly becoming the gold standard for resilient governance.
The Road Ahead: Confidential Governance as a Competitive Advantage
The next phase for DAOs is not simply defending against attacks but proactively building cultures of trust, security, and innovation. Confidential governance models do more than prevent manipulation, they attract top talent by assuring contributors their input is protected from exploitation or backlash.
This evolution also lays the groundwork for regulatory engagement: demonstrating that decentralized communities can self-govern responsibly without sacrificing member privacy opens doors to broader institutional participation.
The momentum behind encrypted DAO voting is unmistakable, and those who move early will define best practices for years to come. For deeper dives on operationalizing these strategies, see our guide on empowering DAOs through encrypted voting.






