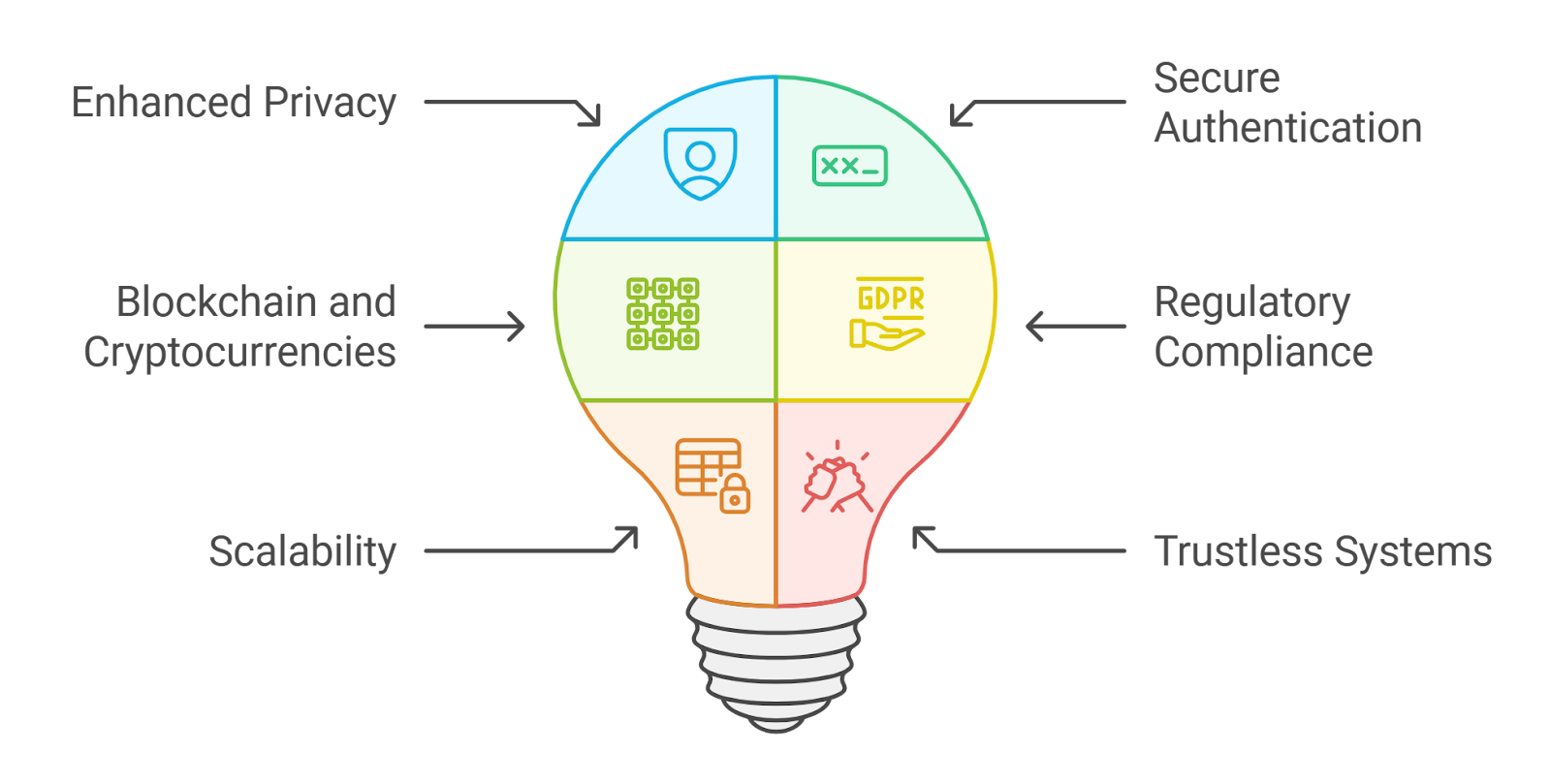
Confidential voting is rapidly emerging as a cornerstone of modern DAO governance, offering a potent blend of privacy and verifiability that addresses some of the most pressing challenges in decentralized decision-making. As DAOs scale and their treasuries and influence grow, the stakes of each proposal and vote increase. Traditional on-chain voting mechanisms, while transparent, often expose voters to undue scrutiny, social pressure, or even targeted manipulation. Confidential DAO voting flips this paradigm by shielding individual choices while still ensuring that every vote is counted accurately and fairly.

Why DAOs Need Private Voting More Than Ever
Public voting records may seem like a feature in decentralized governance, but they come with significant drawbacks. When votes are visible in real-time, participants may be swayed by herd mentality or fear retaliation from larger stakeholders. This can erode the integrity of outcomes and discourage honest participation, especially for controversial or high-value proposals.
Recent advances in shielded voting and zero-knowledge proof voting have made it possible for DAOs to implement secret ballots without losing the transparency that underpins trust in the process. For example, platforms like Snapshot have integrated shielded voting to keep choices private until the tally is revealed, helping protect against manipulation and premature consensus formation.
The Mechanics: How Confidential Voting Works in Practice
The core technologies powering private DAO governance are both elegant and robust:
- Shielded Voting: Votes are encrypted during the process so no one can see how an individual voted until the results are published. This thwarts vote buying, coercion, and last-minute swings based on public sentiment.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): These cryptographic proofs allow voters to demonstrate they have voted validly, without revealing their selection. ZKPs underpin systems like MACI (Minimal Anti-Collusion Infrastructure), which have been successfully piloted by projects such as NounsDAO for truly anonymous yet auditable elections.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This advanced method lets smart contracts tally encrypted votes without ever decrypting them individually. The result? End-to-end confidentiality, even after results go public, offering a new bar for long-term privacy.
Together, these approaches address both sides of the trust equation: they protect individual privacy while guaranteeing that results are verifiable by anyone auditing the blockchain, a critical requirement for legitimacy in decentralized organizations.
Key Benefits of Confidential DAO Voting
-

Protects Voter Privacy: Confidential voting mechanisms like shielded voting and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) ensure that individual choices remain private, reducing the risk of retaliation or social pressure within the community.
-

Prevents Manipulation and Herd Mentality: By encrypting votes until the end of the voting period, systems such as Shutter Network’s shielded voting prevent real-time visibility, helping to stop manipulation, vote buying, and herd behavior.
-

Encourages Honest Participation: Knowing that votes are confidential, community members are more likely to vote according to their true preferences, which leads to more genuine and representative governance outcomes.
-
Maintains Verifiability and Trust: Technologies like zero-knowledge proofs allow all participants to verify that votes are counted correctly without exposing individual choices, preserving both transparency and privacy.
-
Enables Permanent Vote Privacy: Homomorphic encryption allows votes to be tallied without ever decrypting them, ensuring that individual voting choices remain confidential even after results are published.
Market Momentum: Adoption Accelerates Across Leading DAOs
The shift toward verifiable private voting is no longer theoretical. In the past year alone, high-profile DAOs, including NounsDAO and Decent DAO, have rolled out shielded or ZKP-based systems to restore confidence after concerns over declining voter participation and manipulation risks. According to recent updates from Aztec Network and Shutter API integrations, these tools are not only feasible but scalable across diverse governance structures.
This momentum is also being driven by growing awareness of regulatory risks associated with public voter data. By embracing confidential solutions now, DAOs position themselves ahead of potential compliance requirements, while also delivering on their promise of member-centric governance.
The bottom line? Confidential voting is not just about secrecy, it’s about creating an environment where every member feels empowered to participate honestly without fear or compromise. In the next section, we’ll explore how these privacy-preserving technologies maintain ironclad verification standards without sacrificing auditability or legitimacy.
Verification Without Compromise: How Privacy and Auditability Coexist
One of the most persistent misconceptions about confidential DAO voting is that privacy must come at the expense of transparency. In reality, the latest cryptographic solutions elegantly sidestep this tradeoff. Zero-knowledge proof voting, for instance, empowers DAOs to prove that every single vote was cast by an eligible participant and correctly tallied, without ever exposing individual choices or identities. This means any member (or external auditor) can independently verify the integrity of the result, maintaining the core ethos of open, accountable governance.
Technologies like homomorphic encryption push this even further by allowing computations on encrypted data. The votes remain shielded, yet the final tally is mathematically provable and resistant to tampering. This approach is gaining traction in projects focused on DAO privacy solutions that demand both secrecy and robust verification.
For DAOs managing significant treasuries or sensitive proposals, these advances are not just technical upgrades, they’re essential for building durable trust among stakeholders. When members know their votes are both private and provably counted, participation rises and outcomes better reflect the true will of the community.
Practical Challenges: What’s Left to Solve?
Despite rapid progress, confidential voting is not without hurdles. On-chain computational costs for advanced cryptography can be high, especially as DAOs grow in size and complexity. User experience remains another frontier: wallet integrations, seamless interfaces, and clear audit trails all need refinement to make private DAO governance accessible at scale.
Additionally, education is crucial. Members must understand how DAO secret ballots work so they can trust, and confidently use, them. Projects like Oasis Protocol and Aragon are investing heavily in documentation and community onboarding to close this gap.
Key Obstacles to Confidential Voting Adoption in DAOs
-

Technical Complexity of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Integrating ZKPs into DAO voting systems requires advanced cryptographic knowledge and specialized development, which can be a barrier for many organizations. Read more.
-
Scalability and Gas Costs: Confidential voting mechanisms, especially those using ZKPs or homomorphic encryption, often increase computational requirements and on-chain transaction fees, making large-scale votes expensive and slow. Learn about scalability challenges.
-

Usability and User Experience: Shielded voting tools can introduce unfamiliar workflows for voters, leading to confusion or reduced participation if the process is not intuitive. See how Snapshot integrates shielded voting.
-
Transparency vs. Privacy Trade-offs: Some DAO members may be concerned that confidential voting reduces transparency, making it harder to audit individual votes and hold participants accountable. Explore privacy and transparency in DAOs.
-

Integration with Existing Governance Platforms: Adapting confidential voting to established platforms like Snapshot or Aragon can require significant modifications, slowing adoption and increasing risk of incompatibility. Snapshot shielded voting update.
-
Verification and Trust in Results: While zero-knowledge proofs enable verifiable outcomes, some DAO participants may struggle to trust or independently verify cryptographic proofs, potentially undermining confidence in results. Understanding ZKP verification.
It’s also important to recognize that no privacy solution exists in a vacuum. DAOs should combine confidential voting with broader operational security practices, such as encrypted proposal discussions and secure off-chain coordination, to fully realize the benefits of on-chain confidential governance.
The Road Ahead: A New Standard for Decentralized Trust
The coming year will likely see confidential voting become a baseline expectation for reputable DAOs rather than a niche experiment. As regulatory scrutiny sharpens and community expectations evolve, transparent-yet-private voting will define which organizations attract serious contributors, and which are left behind.
If you’re building or participating in a DAO today, now is the time to explore these tools. The shift toward verifiable private voting isn’t just about compliance or optics; it’s about fundamentally strengthening your community’s voice while safeguarding its autonomy.
The future of decentralized governance hinges on our ability to innovate without sacrificing integrity. Confidential voting proves it’s possible to have both ironclad verification and true privacy, a dual promise that will shape the next era of DAO evolution.






