Confidential governance is rapidly emerging as a defining feature in the evolution of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). As the ecosystem matures, privacy-enhancing technologies are not only raising the bar for DAO security but also fundamentally transforming how trust is established and maintained among participants. The shift from fully transparent, on-chain voting to cryptographically protected processes marks a pivotal change in decentralized governance models.
Why Transparency Alone Fails: The Limits of Traditional DAO Governance
Conventional DAO frameworks have long relied on public smart contracts for all governance actions. While this transparency was initially lauded for its openness, it has exposed DAOs to several critical vulnerabilities. Public voting records can lead to coercion, vote buying, and social pressure. Token-weighted voting systems often reveal both voter identities and token holdings, undermining the principle of free and fair participation.
Recent research from MIT’s CSAIL and industry voices like Vitalik Buterin have underscored that true fairness in decentralized organizations demands privacy as much as transparency. Without privacy-preserving mechanisms, DAOs risk entrenching power imbalances and discouraging honest participation, a reality that undermines the very ethos of decentralization.
The Confidential Governance Revolution: Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in Action
In response to these challenges, confidential governance leverages advanced cryptography to secure sensitive operations while preserving verifiability. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), homomorphic encryption, and secure multiparty computation (MPC) are at the heart of this transformation:
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: ZKPs allow members to prove they voted or met participation requirements without revealing how they voted or their token balances.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This technique enables votes or data to be aggregated and counted without decrypting individual inputs, ensuring both accuracy and privacy.
- MPC Frameworks: Solutions like Microsoft’s Confidential Consortium Framework (CCF) allow multiple parties to jointly compute results over encrypted data, without any single party accessing sensitive details.
The Oasis Protocol’s confidential DAO voting infrastructure exemplifies this new paradigm by separating governor contracts from token contracts while integrating ZKP-based workflows. Meanwhile, projects like S2DV use Groth16 zk-SNARKs combined with ElGamal encryption to scale secure voting for large communities without sacrificing confidentiality or computational efficiency.
Building Security and Trust Through Confidentiality
The impact of confidential governance extends beyond technical innovation, it directly strengthens security postures and fosters trust among DAO members. By shielding individual votes from public scrutiny, confidential voting prevents manipulation tactics such as bribery or retaliation. Members can participate authentically, knowing their choices remain private yet verifiable by the network.
This approach also addresses operational risks by keeping sensitive treasury movements or strategic decisions hidden from adversaries while still allowing collective validation through cryptographic proofs. In effect, DAOs adopting these privacy solutions are better equipped to withstand both internal collusion attempts and external exploitation threats.
If you are interested in practical approaches for implementing these technologies within your organization, explore our guide on how confidential governance builds trust in DAOs.
Equitable participation is another crucial benefit of confidential governance. When voting and delegation are private, token holders can express their true preferences without fear of social or economic backlash. This leads to more representative outcomes and reduces the likelihood of governance capture by dominant actors or coordinated cartels. As highlighted in research on private delegation protocols like Kite, privacy-first frameworks empower members to delegate, revoke, and re-delegate voting power seamlessly, without exposing their affiliations or intentions.
Moreover, the scalability of these cryptographic solutions is rapidly improving. Systems such as S2DV demonstrate that confidentiality does not have to come at the expense of performance. By leveraging efficient zk-SNARKs and encryption schemes, large DAOs can now process thousands of votes securely and privately within practical timeframes. This scalability is essential for mainstream adoption as DAOs grow in size and complexity.
For DAO treasuries, confidential governance unlocks new levels of operational security. Private treasury management protocols prevent adversaries from front-running proposals or targeting key stakeholders based on public data. This shields strategic assets while still enabling transparent auditing through selective disclosure mechanisms. If you want to explore how confidential treasuries protect decentralized organizations’ financial interests, see our coverage on confidential DAO treasury strategies.
The Road Ahead: From Niche Feature to Industry Standard
The momentum behind confidential governance is unmistakable. With permanent shielded voting now one of the most requested features in DAO tooling, and vocal support from thought leaders across Ethereum and beyond, the sector is moving toward a new baseline where privacy is not an afterthought but a default requirement.
Top Confidential Governance Protocols for DAOs
-

Oasis Protocol: Implements confidential DAO voting using secure enclaves and privacy-preserving smart contracts. Key features include shielded voting and encrypted ballots, ensuring vote privacy while maintaining verifiability.
-

Zama: Pioneers homomorphic encryption for DAOs, allowing votes and token amounts to remain secret during the entire process. This approach enables end-to-end encrypted voting without revealing individual choices.
-
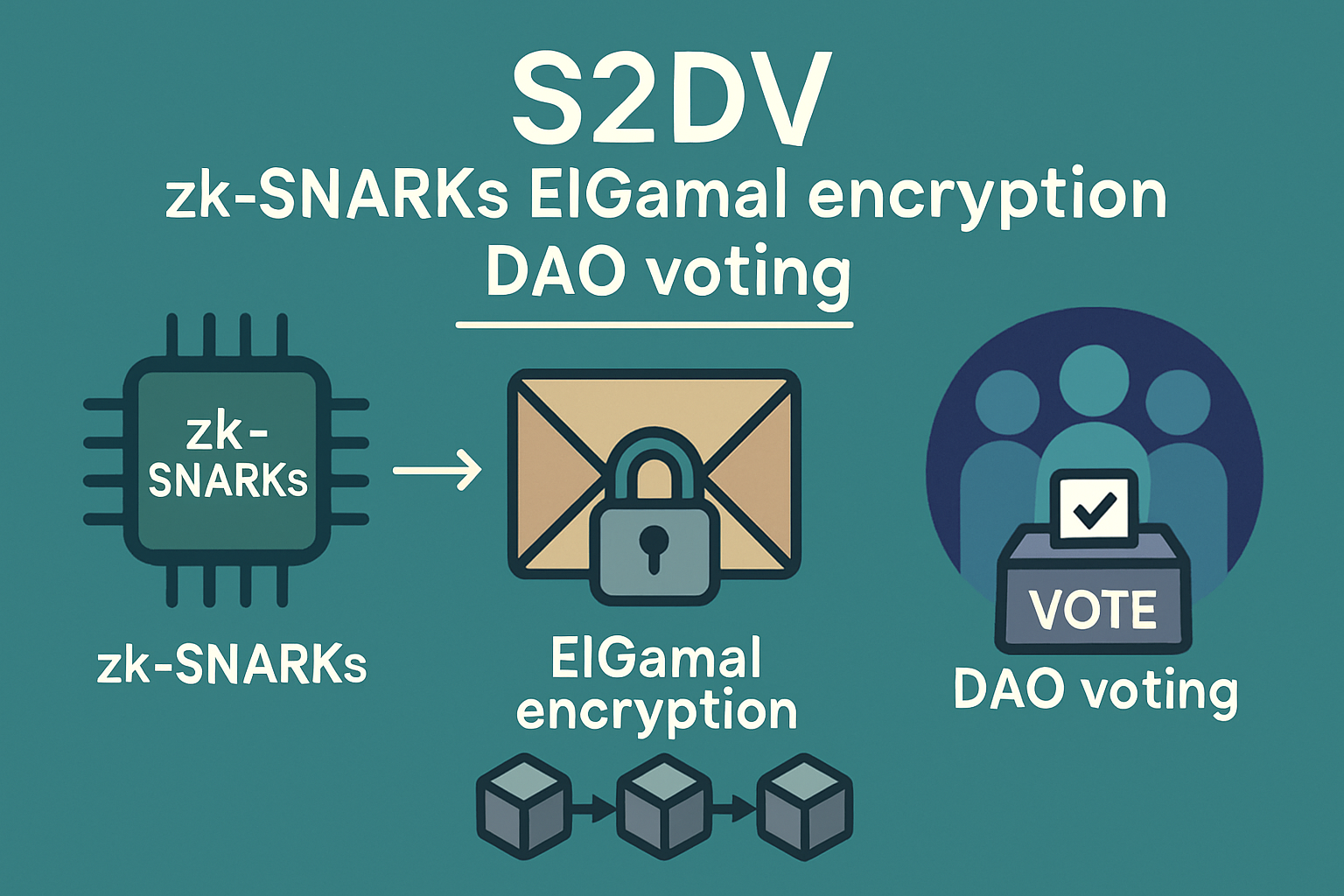
S2DV (Scalable and Secure DAO Voting): Utilizes Groth16 zk-SNARKs and ElGamal encryption to deliver scalable, private, and verifiable voting. Heavy computations are delegated off-chain, while privacy and integrity are preserved on-chain.
Still, implementing these systems requires disciplined architecture choices and ongoing vigilance against emerging attack vectors. DAOs must balance transparency for collective accountability with robust privacy for member protection. The best results come from integrating cryptographic primitives directly into existing governance frameworks rather than relying on bolt-on solutions.
For those building or participating in decentralized autonomous organizations today, embracing confidential governance means investing in both technology and culture, a commitment to secure participation that will define the next era of digital cooperation. As these privacy-enhancing models mature, expect them to set the standard for trust and security across all forms of decentralized coordination.






